Computer Network Security
Computer network security consists of measures taken by business or some organizations to monitor and prevent unauthorized access from the outside attackers.
Different approaches to computer network security management have different requirements depending on the size of the computer network. For example, a home office requires basic network security while large businesses require high maintenance to prevent the network from malicious attacks.
Network Administrator controls access to the data and software on the network. A network administrator assigns the user ID and password to the authorized person.
Aspects of Network Security:
Following are the desirable properties to achieve secure communication:
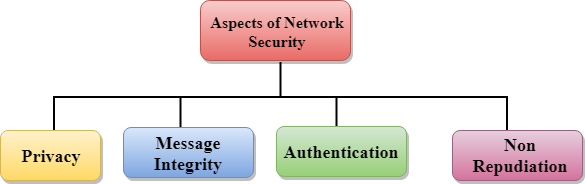
Privacy: Privacy means both the sender and the receiver expects confidentiality. The transmitted message should be sent only to the intended receiver while the message should be opaque for other users. Only the sender and receiver should be able to understand the transmitted message as eavesdroppers can intercept the message. Therefore, there is a requirement to encrypt the message so that the message cannot be intercepted. This aspect of confidentiality is commonly used to achieve secure communication.
Message Integrity: Data integrity means that the data must arrive at the receiver exactly as it was sent. There must be no changes in the data content during transmission, either maliciously or accident, in a transit. As there are more and more monetary exchanges over the internet, data integrity is more crucial. The data integrity must be preserved for secure communication.
End-point authentication: Authentication means that the receiver is sure of the sender?s identity, i.e., no imposter has sent the message.
Non-Repudiation: Non-Repudiation means that the receiver must be able to prove that the received message has come from a specific sender. The sender must not deny sending a message that he or she send. The burden of proving the identity comes on the receiver. For example, if a customer sends a request to transfer the money from one account to another account, then the bank must have a proof that the customer has requested for the transaction.
Active and Passive attacks in Information
Security
Active attacks: An Active attack attempts to alter system resources or affect their operations. Active attacks involve some modification of the data stream or the creation of false statements. Types of active attacks are as follows: Masquerade
Modification of messages
Repudiation
Replay
Denial of Service
Masquerade –
A masquerade attack takes place when one entity pretends to be a different entity. A Masquerade attack involves one of the other forms of active attacks. If an authorization procedure isn’t always absolutely protected, it is able to grow to be extraordinarily liable to a masquerade assault. Masquerade assaults may be performed using the stolen passwords and logins, with the aid of using finding gaps in programs, or with the aid of using locating a manner across the authentication process.

Masquerade Attack
Modification of messages –
It means that some portion of a message is altered or that message is delayed or reordered to produce an unauthorized effect. Modification is an attack on the integrity of the original data. It basically means that unauthorized parties not only gain access to data but also spoof the data by triggering denial-of-service attacks, such as altering transmitted data packets or flooding the network with fake data. Manufacturing is an attack on authentication. For example, a message meaning “Allow JOHN to read confidential file X” is modified as “Allow Smith to read confidential file X”.

Modification of messages
Repudiation –
This attack occurs when the network is not completely secured or the login control has been tampered with. With this attack, the author’s information can be changed by actions of a malicious user in order to save false data in log files, up to the general manipulation of data on behalf of others, similar to the spoofing of e-mail messages.
Replay –
It involves the passive capture of a message and its subsequent transmission to produce an authorized effect. In this attack, the basic aim of the attacker is to save a copy of the data originally present on that particular network and later on use this data for personal uses. Once the data is corrupted or leaked it is insecure and unsafe for the users.

Replay
Denial of Service –
It prevents the normal use of communication facilities. This attack may have a specific target. For example, an entity may suppress all messages directed to a particular destination. Another form of service denial is the disruption of an entire network either by disabling the network or by overloading it with messages so as to degrade performance.

Denial of Service
Passive attacks: A Passive attack attempts to learn or make use of information from the system but does not affect system resources. Passive Attacks are in the nature of eavesdropping on or monitoring transmission. The goal of the opponent is to obtain information that is being transmitted. Types of Passive attacks are as follows: The release of message content
Traffic analysis
The release of message content –
Telephonic conversation, an electronic mail message, or a transferred file may contain sensitive or confidential information. We would like to prevent an opponent from learning the contents of these transmissions.

Passive attack
Traffic analysis –
Suppose that we had a way of masking (encryption) information, so that the attacker even if captured the message could not extract any information from the message.
The opponent could determine the location and identity of communicating host and could observe the frequency and length of messages being exchanged. This information might be useful in guessing the nature of the communication that was taking place.
The most useful protection against traffic analysis is encryption of SIP traffic. To do this, an attacker would have to access the SIP proxy (or its call log) to determine who made the call.

Traffic analysis
ⒸSheikhMuneeb
Message Integrity: Data integrity means that the data must arrive at the receiver exactly as it was sent. There must be no changes in the data content during transmission, either maliciously or accident, in a transit. As there are more and more monetary exchanges over the internet, data integrity is more crucial. The data integrity must be preserved for secure communication.
End-point authentication: Authentication means that the receiver is sure of the sender?s identity, i.e., no imposter has sent the message.
Non-Repudiation: Non-Repudiation means that the receiver must be able to prove that the received message has come from a specific sender. The sender must not deny sending a message that he or she send. The burden of proving the identity comes on the receiver. For example, if a customer sends a request to transfer the money from one account to another account, then the bank must have a proof that the customer has requested for the transaction.
Active and Passive attacks in Information
Security
Active attacks: An Active attack attempts to alter system resources or affect their operations. Active attacks involve some modification of the data stream or the creation of false statements. Types of active attacks are as follows: Masquerade
Modification of messages
Repudiation
Replay
Denial of Service
Masquerade –
A masquerade attack takes place when one entity pretends to be a different entity. A Masquerade attack involves one of the other forms of active attacks. If an authorization procedure isn’t always absolutely protected, it is able to grow to be extraordinarily liable to a masquerade assault. Masquerade assaults may be performed using the stolen passwords and logins, with the aid of using finding gaps in programs, or with the aid of using locating a manner across the authentication process.

Masquerade Attack
Modification of messages –
It means that some portion of a message is altered or that message is delayed or reordered to produce an unauthorized effect. Modification is an attack on the integrity of the original data. It basically means that unauthorized parties not only gain access to data but also spoof the data by triggering denial-of-service attacks, such as altering transmitted data packets or flooding the network with fake data. Manufacturing is an attack on authentication. For example, a message meaning “Allow JOHN to read confidential file X” is modified as “Allow Smith to read confidential file X”.

Modification of messages
Repudiation –
This attack occurs when the network is not completely secured or the login control has been tampered with. With this attack, the author’s information can be changed by actions of a malicious user in order to save false data in log files, up to the general manipulation of data on behalf of others, similar to the spoofing of e-mail messages.
Replay –
It involves the passive capture of a message and its subsequent transmission to produce an authorized effect. In this attack, the basic aim of the attacker is to save a copy of the data originally present on that particular network and later on use this data for personal uses. Once the data is corrupted or leaked it is insecure and unsafe for the users.

Replay
Denial of Service –
It prevents the normal use of communication facilities. This attack may have a specific target. For example, an entity may suppress all messages directed to a particular destination. Another form of service denial is the disruption of an entire network either by disabling the network or by overloading it with messages so as to degrade performance.

Denial of Service
Passive attacks: A Passive attack attempts to learn or make use of information from the system but does not affect system resources. Passive Attacks are in the nature of eavesdropping on or monitoring transmission. The goal of the opponent is to obtain information that is being transmitted. Types of Passive attacks are as follows: The release of message content
Traffic analysis
The release of message content –
Telephonic conversation, an electronic mail message, or a transferred file may contain sensitive or confidential information. We would like to prevent an opponent from learning the contents of these transmissions.

Passive attack
Traffic analysis –
Suppose that we had a way of masking (encryption) information, so that the attacker even if captured the message could not extract any information from the message.
The opponent could determine the location and identity of communicating host and could observe the frequency and length of messages being exchanged. This information might be useful in guessing the nature of the communication that was taking place.
The most useful protection against traffic analysis is encryption of SIP traffic. To do this, an attacker would have to access the SIP proxy (or its call log) to determine who made the call.

Traffic analysis
ⒸSheikhMuneeb


